6 beste netwerkbeheertools die prestaties bijhouden
De markt voor netwerkbeheersoftware is erg druk. Verkort uw zoekopdracht door onze aanbevelingen van de beste netwerkbeheertools te volgen.
IIS , een afkorting voor Internet Information Services , en voorheen bekend als Internet Information Server, is een webserver van Microsoft die is ontworpen voor gebruik met Windows-producten, te beginnen met de NT-familie.
Deze webserver wordt gebruikt om Windows-gebruikers te helpen bij het hosten van verschillende soorten inhoud op internet, zoals mediabestanden, documenten of zelfs volwaardige websites. Op dit moment is Apache de meest populaire Windows-webserver, op de voet gevolgd door IIS, wat behoorlijk indrukwekkend is.
Wat is IIS?
IIS is een webserver waarmee u gemakkelijk vertrouwd kunt raken, dankzij de intuïtieve grafische gebruikersinterface (GUI) waarmee u websites kunt beheren die aan de service zijn gekoppeld en de bijbehorende gebruikers . De GUI van IIS maakt het gemakkelijk om websites vanaf één locatie te ontwerpen, aan te passen, te configureren en te publiceren.
Het heeft een ingebouwde tool voor websitebeheer, IIS Manager genaamd, die u kunt gebruiken om opties aan te passen, zoals beveiligingsinstellingen, prestatieparameters, logboekvoorkeuren, evenals foutpagina's of standaardwaarden voor de websites die u beheert.
Vanuit technisch oogpunt is IIS behoorlijk veelzijdig, aangezien het zowel standaard als dynamische webpagina's kan bedienen, zonder noemenswaardige inspanning. U kunt het dus gebruiken om HTML-webpagina's te maken en te publiceren, maar het is fijn om te weten dat u ook PHP-pagina's en ASP.NET-toepassingen kunt beheren.
Dankzij zijn flexibiliteit kan IIS scripts en toepassingen in dynamische webpagina's uitvoeren en de resultaten weergeven op het webbrowserscherm van de bezoeker. Met statische websites is het proces nog eenvoudiger: IIS stuurt de HTML-inhoud en afbeeldingen (indien aanwezig) gewoon naar de webbrowser van de bezoeker.
Wat is het doel van IIS?
Aangezien het profiteert van de volledige ondersteuning van Microsoft en het feit dat het tal van geavanceerde functies bevat, is IIS een uitstekende keuze voor het maken en beheren van commerciële websites, zoals e-shops of promotionele portfoliowebsites.
Het nadeel is dat het gebruik van IIS voor commerciële doeleinden ook betekent dat je een commerciële licentie nodig hebt. Bovendien varieert de prijs van dit licentietype afhankelijk van het aantal gebruikers dat u wilt opnemen.
We hebben dus al vastgesteld dat IIS kan worden gebruikt om een website te maken en te hosten, en dat het statische en dynamische webinhoud ondersteunt. IIS is echter veel meer dan dat. U kunt bijvoorbeeld de ingebouwde moduleondersteuning gebruiken om de functionaliteit van uw server te verbeteren.
Het is mogelijk om streamingmodules op uw server te installeren, zodat de bezoekers van uw website kunnen profiteren van streaming media-inhoud. U kunt ook een module voor URL-herschrijving gebruiken waarmee u krachtige URL-implementatieregels kunt maken, zodat bezoekers ze gemakkelijk kunnen onthouden en zoekmachines ze sneller kunnen vinden.
Daarom is het vanzelfsprekend dat als je een snelle manier nodig hebt om een website te maken en te publiceren, IIS een van de beste manieren is om dit te doen. De allerbeste manier blijft nog steeds Apache HTTP, omdat het open-source is en je het gratis kunt gebruiken, ongeacht het aantal gebruikers.
IIS-versiegeschiedenis
Vermeldenswaard is dat IIS in eerste instantie bedoeld was als alternatief voor een webserver die als onderzoeksproject was ontwikkeld. Het eerste door Microsoft ondertekende webserverproject werd gedistribueerd als freeware en was ontworpen voor EMWAC (Europees Microsoft Windows NT Academisch Centrum).
Aangezien de EMWAC-server echter niet alle verkeersvolumes die naar de website microsoft.com gingen, aankon, werd het project stopgezet en ontwikkelde Microsoft een eigen webserver in de vorm van IIS.
Een opmerkelijk aspect is dat de meeste versies van IIS zijn uitgebracht met of naast een versie van het Windows-besturingssysteem. Zeker, toen was IIS slechts een schaduw van hoe we het vandaag kennen; in feite zou elke Windows-release heel goed kunnen dienen als een controlepunt voor de evolutie van IIS.
Als u van plan bent om IIS te gebruiken, probeer dan de nieuwste stabiele versie te gebruiken, aangezien deze meestal de strengste beveiliging heeft en de beste prestatiegerichte resultaten oplevert, vooral als u de nieuwste versie van Windows of Windows Server gebruikt.
Hoe IIS installeren?
Zoals we eerder hebben vermeld, hoeft u IIS niet te installeren, omdat het eigenlijk bij uw Windows-versie zou moeten worden geleverd. Als u Windows 10 gebruikt, zou er al een versie van IIS 10.0 op uw pc beschikbaar moeten zijn.
Microsoft heeft echter besloten om IIS niet standaard te activeren, dus u moet het handmatig inschakelen. Maar maak je geen zorgen, het is niet bepaald een raketwetenschap om dit voor elkaar te krijgen. Volg deze stappen om IIS op uw pc te activeren:
Nu wilt u misschien uw pc opnieuw opstarten, zodat uw systeem alle vereiste configuratiebestanden kan laden en u IIS volledig kunt gebruiken. Het kan ook werken zonder uw pc opnieuw op te starten, maar uw systeem opnieuw opstarten nadat u een nieuwe functie hebt ingeschakeld, is nooit een slecht idee.
U kunt IIS ook op uw computer inschakelen met PowerShell. Als je er nog nooit van hebt gehoord, is PowerShell een complexe tool die door velen wordt aangezien voor CMD. PowerShell is veel complexer dan dat, maar we zullen niet te veel in detail treden. Zonder verder oponthoud, hier is hoe u IIS op uw Windows-pc kunt inschakelen met PowerShell:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature –online –featurename IIS-WebServerRoleZoals u kunt zien, geeft PowerShell aan dat opnieuw opstarten niet nodig is na het inschakelen van IIS op uw Windows 10-pc. Als u het proces wilt terugdraaien, kunt u de volgende opdracht gebruiken om IIS met PowerShell uit te schakelen:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature –online –featurename IIS-WebServerRoleHoud er echter rekening mee dat zelfs PowerShell u aanbeveelt om uw pc opnieuw op te starten om deze functie uit te schakelen. Het is ook mogelijk om het later opnieuw op te starten, maar start in de tussentijd geen nieuwe projecten.
Hoe werkt de IIS-server?
Eerst en vooral is het vermeldenswaard dat IIS zijn eigen procesengine heeft die voor alle client-serververzoeken kan zorgen. Daarom, wanneer een client een verzoek naar uw webserver stuurt, verwerkt IIS dat verzoek, genereert een antwoord en stuurt het naar de client.
Vanuit architectonisch oogpunt ontvouwt dit proces zich op twee verschillende lagen:
Zoals we hierboven hebben vermeld, kunt u HTTP.SYS vinden in de kernelmodus. HTTP.SYS wordt gebruikt om clientverzoeken door te sturen naar een toepassingsgroep. Dit proces voor het doorsturen van verzoeken wordt gestart wanneer de klant interactie heeft met de URL van de website en probeert toegang te krijgen tot de pagina. Telkens wanneer dit gebeurt, haalt HTTP.SYS de verzoeken van de client op en zet deze in de wachtrij voor specifieke groepen van toepassingen.
Na het doorsturen van het verzoek laadt w3wp.exe (het werkproces ) het ISAPI- filter en laadt HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest op zichzelf, of in combinatie met aspnet_isapi.dll als het een ASPX-pagina is. De lancering van HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest markeert het begin van de verwerking, waarna het HttpRuntime- proces HttpApplication- objecten gebruikt om een pool te bouwen, waarvan de inhoud via HTTP wordt doorgegeven.
De HTTP-modules worden vervolgens geactiveerd en dit proces gaat door totdat het verzoek bij de HTTP-handler van de ASP.NET- pagina terechtkomt. Nadat het verzoek de HTTP-route heeft doorlopen, wordt de pagina weergegeven.
Wat is het werkproces?
Allereerst is het vermeldenswaard dat er niet slechts één werkproces is. In feite zijn er verschillende van dergelijke entiteiten die zorgen voor de goede werking van uw webserver en de inhoud die u erop host, of het nu gaat om websites of applicaties waar we het over hebben.
De werkprocessen van IIS zijn dus verantwoordelijk voor het leveren van de uitvoeringsomgeving voor alle applicaties en websites die u eerder in de IIS hebt geconfigureerd. Deze processen bevatten verschillende stukjes informatie die cruciaal zijn voor het goed functioneren van de bovengenoemde diensten.
Het is mogelijk dat u de API kunt gebruiken om informatie op te halen met betrekking tot geheugenvoetafdruk of CPU-gebruik. Deze details kunnen u helpen de algehele gezondheid van uw webserver en de bijbehorende werkprocessen nauwlettend in de gaten te houden.
Last but not least kunt u de API gebruiken om werkprocessen te beëindigen door simpelweg een DELETE- verzoek naar het eindpunt van werkprocessen te sturen.
Wat is de applicatiepool?
Hoewel de naam enigszins voor zich spreekt, is het doel van de Application Pool van IIS veel complexer. Eerst en vooral bevat de Application Pool de werkprocessen, dus het is veilig om te zeggen dat het de rol van een container speelt. Bovendien isoleert het applicaties van elkaar, of ze nu op dezelfde server draaien of op aparte servers, wat in strijd is met hoe een pool gewoonlijk werkt.
Het is vrij belangrijk om te weten dat een enkele applicatiepool meerdere websites kan bevatten. Met andere woorden, je kunt zeggen dat een applicatiepool slechts een set URL's is die door werkprocessen is afgehandeld. De scheiding van applicaties in deze pools wordt gerechtvaardigd door het feit dat het het beheer aanzienlijk zou kunnen vereenvoudigen. Meer nog, het is vanwege deze isolatie dat, in het geval dat één applicatiepool faalt, de andere gewoon door kunnen gaan.
Hoe een IIS-server configureren?
Je hebt IIS op je computer ingeschakeld en je hebt wat geleerd over de componenten ervan. Laten we nu eens kijken hoe je het correct kunt configureren, zodat je zonder noemenswaardige inspanningen je eigen webserver kunt draaien.
Zoals we een tijdje geleden al zeiden, is een van de belangrijkste redenen waarom mensen IIS gebruiken, de eenvoudige implementatie van webapplicaties. Met IIS en de Advanced Installer-functie kunt u web-apps configureren en implementeren op verschillende servers zonder een slag over te slaan. U hoeft ook niet voor elke machine nieuwe configuraties aan te maken, aangezien IIS daar gemakkelijk voor kan zorgen.
Als u een nieuwe website wilt configureren, moet u eerst naar de weergave Bestanden en mappen gaan, waar u bestaande toepassingsbestanden kunt beheren of desgewenst nieuwe kunt toevoegen. Houd er rekening mee dat u uw toepassingsbestanden in hun individuele map moet plaatsen, aangezien het beheerderspaneel van uw website er later gebruik van zal maken.
Als u eenmaal voor de bestanden hebt gezorgd, kunt u naar de IIS-serverweergave gaan, waar u de werkbalk Nieuwe website kunt gebruiken om de naam van uw nieuwe website in te voeren. Wat u vervolgens moet doen, is de HTTP/HTTPS- instellingen van uw website aanpassen en overwegen om SSL te gebruiken voor extra beveiliging. Zo kunt u HTTP en SSL configureren voor uw website of map:
Hoe kan ik een IIS-webserver beveiligen met SSL?
SSL, wat een afkorting is voor Secure Sockets Layer, is nog steeds een van de beste manieren om communicatie tussen u en een doelwebsite te versleutelen. Weet je nog dat een tijdje terug veel websites de sprong maakten van HTTP naar HTTPS? Welnu, SSL-certificaten waren en zijn nog steeds een essentieel onderdeel van dit proces.
het goede nieuws is dat u SSL vrij eenvoudig op uw website kunt implementeren met IIS. Aan de andere kant zul je zeker een certificaat moeten kopen, omdat dit de enige manier is waarop je website als betrouwbaar kan worden erkend vanuit het oogpunt van gegevenscodering.
Therefore, the first step would be finding an SSL certificate provider and purchase such an item. After the purchase, you’ll receive either a code or a certificate file. In order to configure SSL with IIS we’ll need the certificate file, so make sure you retrieve it before moving on.
Secure IIS web server with SSL
Now you’ve successfully installed a certificate for your IIS server. However, that’s not nearly enough, as you’ll still have to bind the certificate for your website. By the end of it, you’ll have a secure website with a certificate that’s associated with your website, port, and IP address.
Bind security certificate to the website
So we’ve managed to install SSL on your IIS web server and associate it with your website. You can use the steps above to associate certificates with more than just one website if the need arises. However, there’s still one thing we need to do: redirect incoming HTTP traffic to HTTPS, to ensure encryption of our visitors’ traffic.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
(.*) in the Pattern field{HTTPS} in the Condition input field^OFF$ in the Pattern fieldhttps://{HTTP_HOST}/{REQUEST_URI} in the Rewrite URL fieldThat’s it, you’ve now completely implemented SSL on your web server, bound it to your website, and configured the site to redirect incoming HTTP traffic to HTTPS. If done correctly, visitors who try to access your website using HTTP will be automatically redirected to its secure HTTPS counterpart.
What are Virtual Directories?
As we’ve established before, creating and managing a website isn’t the only thing that IIS is capable of doing. You can also create applications, which we already mentioned, but most importantly, you can create virtual directories by simply giving them a name that maps them to a physical directory.
The way this feature works is by letting users access various types of content that are hosted on a server quickly through a direct name. Surely enough, this content could be a website, but it could also be photos, videos, or other types of smaller media files.
Back in the day when IIS 6.0 was all the fuss, virtual applications, and directories were treated as separate objects by IIS. As such, applications consisted of the following elements:
Starting with IIS 7.0, virtual applications and directories are organized within a hierarchy, but they’re still considered to be separate objects. Thus, a website, which is higher in the hierarchy, can contain several applications, or virtual directories that are mapped to a physical location on your PC.
What are log files in IIS?
In IIS log files serve the same purpose they do wherever else you may encounter them. You can use these files to check how things unfolded on your web server, see important events, and, most importantly, understand where things went wrong if any malfunction occurs.
In other words, an IIS log file keeps tabs on everything that happens to your web server, in case you ever need it. A few examples of recorded data include the precise date and time of the events, how much data was transmitted, and the IP addresses related to the events.
Find log files on IIS 7.0 and later
Find log files on IIS 6.0 and earlier
Can I change ports in IIS?
IIS uses port 80 for all HTTP traffic by default, but that doesn’t mean you can’t change it to another value if you want or need to. Changing to a different port can help you avoid certain firewall-related connectivity issues or dodge attacks that target certain service-port vulnerability combos.
Change default port in IIS
Since IIS usually uses port 80 by default, there’s no need to specify it whenever you want to test your website’s functionality, for instance, from inside a browser. You just type your domain name and you should be able to access your website without a hiccup.
However, if you insist on changing the default port, you’ll need to specify it each time you’re trying to access your website from a web browser. You can do that by adding :port number (where port number is the actual port you’re using) at the end of your domain name.
If, for instance, we would change the port of our website to, let’s say 2609, accessing it would look like this: Tips.WebTech360.com:2609. Pretty simple, right?
Now if you’re using an older version of Windows, and implicitly an older version of IIS, there are a few things you’ll need to do in a different manner to change the default port.
Change IIS port on Windows 8.1
How can I monitor IIS?
If you’re not exactly a fan of keeping things in order through manual testing and checking log files frequently (we get you), you may want to consider leaning on third-party software solutions that could keep an eye on your IIS web server for you.
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor
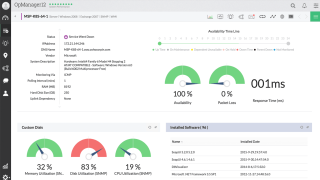
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor is currently one of the best third-party utilities that can help you monitor your IIS website, server, application, or virtual directory without significant efforts. You just point it to the things you want to keep track of and let it work its magic.
Not only does this tool let you know if your websites and web servers are up and running, but it also provides you with an impressive range of key metrics, including but not limited to CPU, memory & disk usage, and response times.
Furthermore, if there’s something wrong with one of the websites you’re monitoring, SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor can automatically restart it for you in an attempt to fix the issue in a simple manner.
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor’s screen is split into multiple sections, where you can monitor and analyze your applications and websites, access an overview of your applications’ health status displayed in graph form, and even manage applications at the press of a button.
You can also use this tool to keep track of your SSL certificates‘ expiration dates so that you can always be on top of things when it’s time to renew a soon-to-expire certificate. More so, you can use SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor to manage SSL certificates for several websites or servers for added convenience.
If you’re curious and want to give SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor a try, you’ll be glad to know that there’s a 30-day free trial available, so that you can test run its capabilities before committing to purchasing a license.
What is IIS – Conclusion
To wrap it up, IIS is a handy Microsoft webserver service you can use to create your own server, as well as manage websites, applications, and virtual directories in it without breaking a sweat. It’s currently the second most popular Windows web server in the world, losing first place to Apache HTTP, which is a completely free alternative.
IIS is mainly used to manage commercial websites, which requires you to purchase a commercial license. The price of such a license varies depending on the number of users you plan on having on the website.
Configuring IIS is somewhat intuitive, but you’ll need to be a bit tech-savvy to be able to make out all of its features, understand what each of them does and configure them to get the most out of your web server and associated websites or applications.
De markt voor netwerkbeheersoftware is erg druk. Verkort uw zoekopdracht door onze aanbevelingen van de beste netwerkbeheertools te volgen.
Ping-sweeps kunnen op veel manieren in uw voordeel worden gebruikt. Lees verder terwijl we bespreken hoe en introduceer de 10 beste Ping-sweep-tools die u kunt vinden.
Websites zijn belangrijk en moeten voortdurend nauwlettend worden gecontroleerd op adequate prestaties. Hier zijn enkele van de beste tools voor het monitoren van websites.
Hier is een blik op enkele van de allerbeste software-implementatietools om de pijn van het beheer van een willekeurig aantal machines te verlichten
sFlow is een stroomanalyseprotocol dat in tal van netwerkapparaten is ingebouwd. We bekijken de top vijf van beste gratis sFlow-verzamelaars en -analysers.
Nu Linux steeds populairder wordt in datacenters, hebben we gekeken naar het monitoren van bandbreedte op Linux en zijn ook de beste tools aan het beoordelen.
E-mailbeveiliging is een belangrijke taak van managed service providers. We waren bezig met het beoordelen van SolarWinds Mail Assure, een van de beste tools voor dat doel.
Als u een krachtige Windows-gebruiker bent, weet en begrijpt u waarschijnlijk hoe het uitvoeren van verschillende bewerkingen op uw pc meer dan één benadering en
Windows-netwerkmonitor vereist tools met beperkte vereisten. Vandaag keken we naar de beste hulpprogramma's voor netwerkbewaking voor Windows 10.
Latency lijkt de grootste vijand van netwerken te zijn. Deze latency-meettools leren hoe latency te testen om problemen op te sporen, te lokaliseren en op te lossen.