Imagine having the ultimate control over your Windows 11 machine, executing powerful scripts and commands that can automate tasks, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance—all with just a few keystrokes. That's the magic of using Windows 11 PowerShell as administrator. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, IT professional, or someone looking to level up your PC management skills, mastering PowerShell as administrator opens doors to efficiency and precision. In this guide, we'll dive straight into the essentials, keeping things focused and actionable so you can start commanding your system confidently right away. Let's get you elevated and empowered! 🚀
Why Use PowerShell as Administrator in Windows 11?
PowerShell isn't just a command-line tool; it's a powerhouse for automation and system management in Windows 11. Running it as administrator grants elevated privileges, allowing you to access restricted areas like system files, registry edits, and advanced configurations that standard users can't touch. This is crucial for tasks such as installing software silently, managing services, or diagnosing hardware issues.
Without admin rights, you'll hit roadblocks—think "Access Denied" errors that frustrate even seasoned users. By learning to run PowerShell as administrator, you'll bypass these limitations, saving time and reducing headaches. Plus, in the latest Windows 11 updates, PowerShell has evolved with better integration for cloud services and AI-driven scripting, making it more relevant than ever for modern workflows.
Step-by-Step: How to Open PowerShell as Administrator in Windows 11
Getting started is straightforward. Follow these steps to launch PowerShell as administrator quickly. We'll cover multiple methods so you can choose what fits your style—whether you're on a desktop, laptop, or even a touch-enabled device.
- Using the Start Menu (Quickest for Beginners)
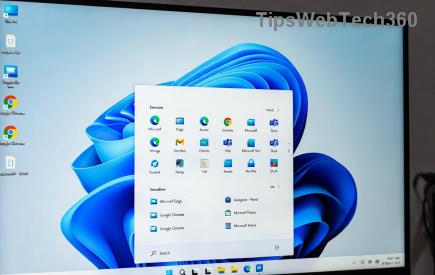
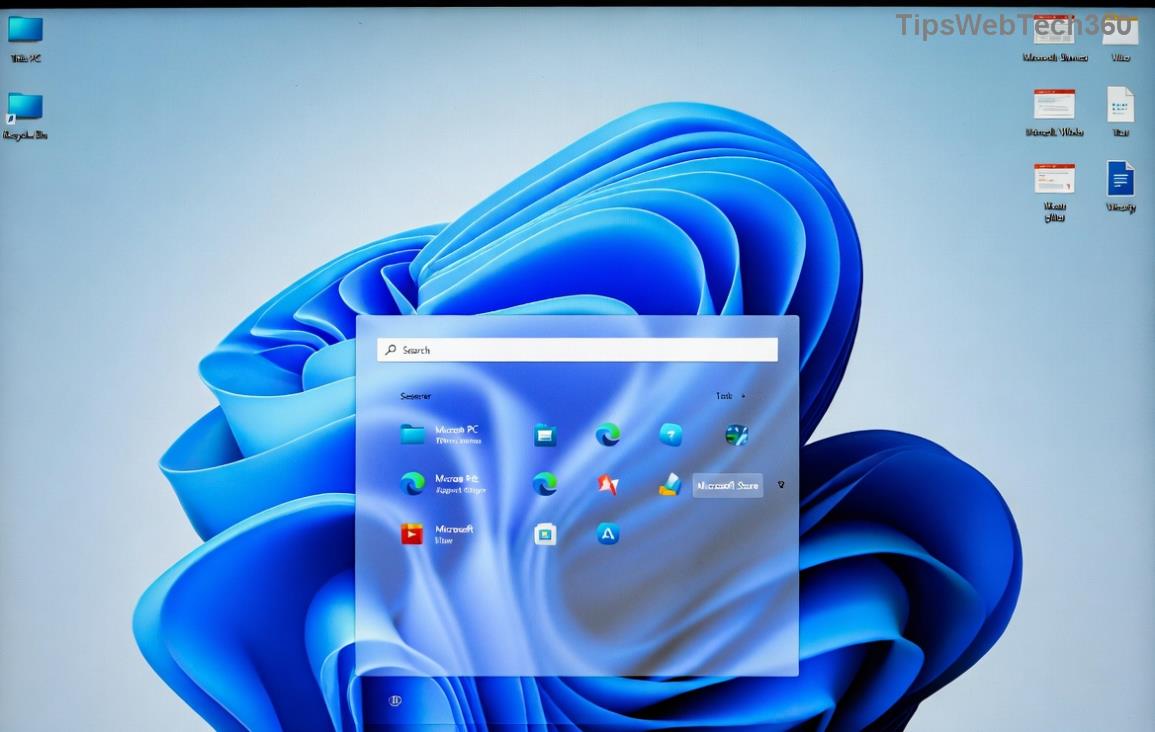
Click the Start button (Windows icon) on your taskbar. Type "PowerShell" in the search bar. When the result appears, right-click on "Windows PowerShell" and select "Run as administrator". Confirm any User Account Control (UAC) prompt by clicking "Yes". Boom—you're in! This method is perfect for one-off tasks and works seamlessly in the latest Windows 11 builds.
- Via the Run Dialog (For Speed Demons)
Press Windows key + R to open the Run box. Type "PowerShell" and hold down the Ctrl + Shift keys while pressing Enter. This combo forces elevated mode. Hit "Yes" on the UAC dialog, and you're ready to roll. Pro tip: Pin this shortcut to your taskbar for even faster access next time.
- From the Task Manager (Advanced Recovery)
If your system is sluggish, open Task Manager with Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Go to the "File" menu, select "Run new task", type "PowerShell", check the "Create this task with administrative privileges" box, and click OK. Ideal for troubleshooting without restarting.
Once open, you'll notice the window title says "Administrator: Windows PowerShell". That's your cue that elevated mode is active. If you're new to this, don't worry—the interface is intuitive, with a blue background and prompt ready for your commands.

Essential Commands for PowerShell as Administrator
Now that you're in, let's put that power to use. Here are some must-know PowerShell commands that shine under administrator privileges. These are curated for practicality, helping you manage your system efficiently without fluff.
- Get-Process | Stop-Process -Name "AppName": Force-close stubborn apps or processes that won't quit normally. Replace "AppName" with the target, like "notepad". Great for freeing up resources instantly. ⭐
- Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned: Enable script execution safely. This is a game-changer for automating repetitive tasks, but use it wisely to avoid security risks.
- dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth: Repair Windows components. Run this as admin to fix corruption issues that standard tools can't touch—essential for maintaining a smooth Windows 11 experience.
- Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq "Stopped"} | Start-Service: Restart critical services. Perfect for IT pros troubleshooting network or security features.
For a quick reference, here's a handy table of common admin-level commands:
| Command |
Purpose |
Example Use Case |
| sfc /scannow |
Scans and repairs system files |
Fix corrupted files after a crash |
| Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux |
Enables WSL for Linux integration |
Set up dual-boot-like environments |
| New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow Port 80" -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 80 -Action Allow |
Configures firewall rules |
Open ports for web servers |
| Update-Help |
Refreshes PowerShell help files |
Stay current with command documentation |
These commands are battle-tested in the most recent Windows 11 iterations, ensuring compatibility and reliability. Experiment in a safe environment first to build confidence.

Pro Tips and Best Practices for Safe PowerShell Admin Usage
To keep things smooth and secure, always run PowerShell as administrator only when necessary—elevated mode can accidentally alter system settings if mishandled. Here are focused tips to elevate your game:
- Create a Custom Shortcut: Right-click on your desktop, select New > Shortcut, enter "PowerShell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass", and finish the setup. Right-click the shortcut, go to Properties > Advanced, and check "Run as administrator". This saves time for frequent users. 👍
- Enable Logging for Auditing: Use Start-Transcript -Path C:\Logs\PowerShellLog.txt at the start of sessions. It records everything, helping you track changes or debug scripts—vital for professional setups.
- Integrate with Task Scheduler: Automate admin tasks by scheduling PowerShell scripts. Search for "Task Scheduler" in Start, create a basic task, and set it to run with highest privileges. Imagine backups or updates happening effortlessly!
- Handle UAC Smartly: If UAC prompts annoy you, adjust settings via secpol.msc (run as admin), but never disable it entirely—security first! 😊
For deeper dives, check out Microsoft's official documentation on PowerShell scripting. It's a goldmine of updated resources tailored for Windows 11.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even pros slip up sometimes. Watch out for these traps when using PowerShell as administrator:
- Execution Policy Errors: If scripts won't run, verify your policy with Get-ExecutionPolicy and adjust as needed. Avoid "Unrestricted" for security reasons.
- Path Issues: Commands failing? Use full paths or $env:PATH to check your environment. This keeps things running smoothly.
- Module Conflicts: In multi-user setups, ensure modules like Active Directory are imported correctly with Import-Module. Test in a virtual machine if possible.
By steering clear of these, you'll maintain a frustration-free experience. Remember, practice makes perfect—start small and scale up.
What's Next? Level Up Your PowerShell Skills
You've now got the tools to harness Windows 11 PowerShell as administrator like a boss. From quick launches to powerful commands, you're set to tackle any system challenge. But why stop here? Explore scripting for automation, integrate with Azure for cloud management, or even build custom modules. The possibilities are endless, and each step builds your expertise further. Dive in, experiment, and watch your productivity soar. If this guide sparked your interest, share your favorite command in the comments—what will you automate first? Let's keep the conversation going! 👏